ALL ABOUT COTTON
What you need to know about textile fibers, the history cotton, how it's cultivated, spun and finally knitted into L'Envers favorites.
1. Textile fibers
Textile fibers are generally classified into three main categories: synthetic, artificial and natural fibers. Each of these categories has unique characteristics that influence their use in the fashion and textile industry.
Synthetic fibers, such as polyester, polyamide or elastane, are man-made fibers from chemical compounds, such as petroleum or coal. Both in their manufacturing process and in their use throughout their life cycle, these fibers are extremely polluting. In fact, being composed of polymers, these fibers release thousands of plastic micro particles each time you wash your item. Their composition also makes them polluting right up to the end of their life because they are not biodegradable and difficult to recycle.
Artificial fibers are man-made from natural raw materials transformed using chemical processes. For example, Lyocell is an artificial fiber of natural and plant origin made from wood pulp, usually from eucalyptus trees, which is then chemically treated to obtain a soft, silky textile fiber that resembles silk. Their manufacturing often involves complex chemical processes that can generate toxic waste and pollutants that damage our ecosystem.
Finally, natural fibers come from natural raw materials and are not transformed by man. They can be of plant origin, such as cotton, linen or even nettle, or of animal origin such as silk or wool. Cotton is one of the most commonly used natural fibers around the world, and particularly popular in the textile industry. Soft, breathable and absorbent, cotton is ideal for making comfortable, lightweight clothing.
2. The history of cotton
The first traces of the use of cotton date back to around 5000 BC, where it was cultivated and woven in India and Egypt.
Its use quickly spread to other regions of the world, notably Asia and the Middle East. Cotton was introduced to Europe through trade with India and other parts of the Orient.
Over the following centuries, its popularity continued to grow in Europe, where it became a luxury item favored by the wealthy classes. Then the industrial revolution and the invention of machines such as the mechanical loom allowed massive production of cotton fabrics at much lower costs, beginning the democratization of this fiber.
In the 20th century, hardier and more productive varieties of cotton were developed through hybridization and genetic selection techniques. Today, cotton is grown in many countries around the world, with significant production in China, India, the United States, Pakistan and several African countries.
3. The differences between organic and conventional cotton
Although cotton remains one of the most popular and widely used fibers in the world, its production poses enormous sustainability challenges. Intensive cotton cultivation causes deforestation, soil degradation and excessive use of water and chemicals.
Therefore, at L’Envers, we have chosen 100% organic cotton.
It is cultivated using an organic farming method which aims not to use any pesticides, insecticides, chemical fertilizers or genetic modifications. Its cultivation is therefore more sustainable than conventional cotton because it does not pollute ecosystems. In addition, this type of agriculture requires much less water because the soils are richer and retain more rainwater.
The cotton is then harvested manually, which guarantees better quality of the fiber and therefore of our pieces.
Cotton being a natural fiber, this allows us to offer pieces that are both hypoallergenic, breathable and healthy for our skin and our planet!
4. The transformation process of L'Envers cotton yarn
The cotton transformation process is carried out in several stages, from growing the plant to manufacturing our pieces.
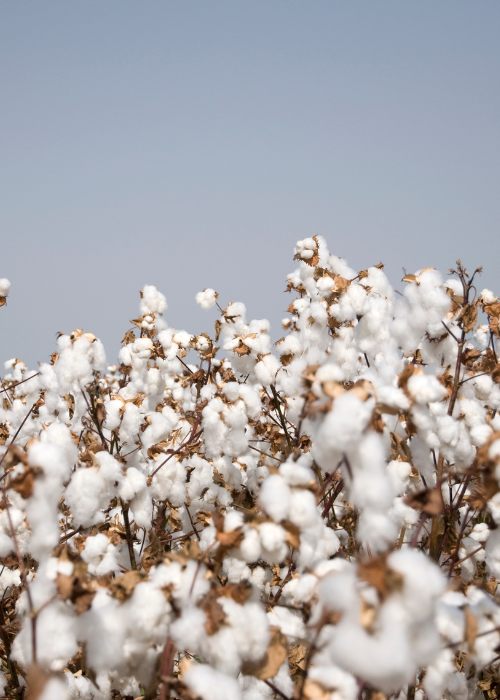
Our cotton is grown in India, and more precisely in Punjab, where the climatic conditions are suitable for the growth of the plant, in particular thanks to the heavy rains allowing natural irrigation. Farmers plant cotton seeds and grow them until they reach maturity: the cotton flowers then bloom and allow us to harvest the fiber. During the harvest, farmers then collect the cotton ball made up of cotton seeds and fibers.
It is during ginning that the cotton fibers are separated from the rest of the ball, and then cleaned to remove impurities such as dirt, leaves and plant debris. Organic cotton does not use any chemicals to do this.
Once clean, the cotton fibers are carded and combed, that is to say they are aligned all in the same direction in order to eliminate the last impurities and facilitate spinning. They are then stretched and twisted to obtain our cotton thread.
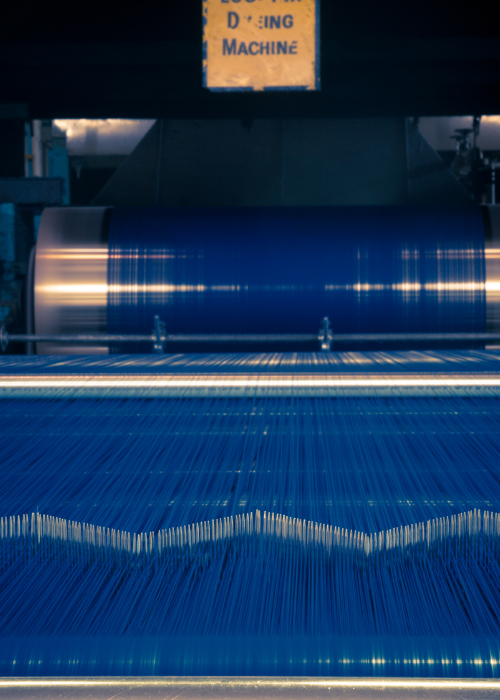
Our yarn is then dyed in Portugal with OEKO-TEX® STANDARD 100 certified reactive dyes which allow for shorter dyeing cycles and the water is recycled in a closed cycle after each dye bath.
The dyed yarn is then shipped to Béjar, Spain to our artisan Miguel Angel who places the spools of dyed yarn on his linear knitting machines to be able to individually make each of our pieces.
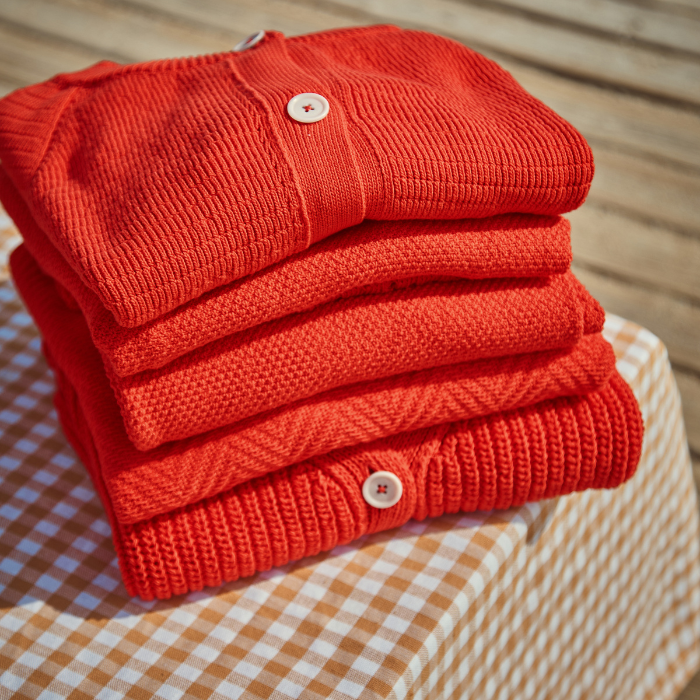
5. Our cotton collection
L'Envers cotton pieces are made from a yarn made from 100% GOTS certified organic cotton.
The cotton we use grows in India. It is first spun in India and then dyed in Portugal. All parties involved in its production are OEKO-TEX® STANDARD 100 and GOTS certified, and are audited every year to ensure compliance with working conditions and other regulations required by these certifications. Our spinner is also invested in creating a positive social impact with efforts such as its participation in Cotton For Life, a CSR program which aims to promote sustainable fashion by creating a transparent, eco-friendly textile value chain. The yarn is then sent to our artisan, Miguel Angel, who makes your pieces one by one with the greatest care in his workshop in Béjar, near Madrid, where we are based.
We offer different colors for our organic cotton. Each color results from a dyeing process with OEKO-TEX® STANDARD 100 certified reactive dyes which reduce the energy consumed by involving shorter dyeing cycles, as well as the recycling and reuse of this resource in a closed cycle. Our off-white cotton is undyed, which makes the piece even more natural.
Soft and comfortable, this natural material is hypoallergenic, healthy for the skin and breathable!
Easy to maintain, cotton can be washed both by hand and in the machine. Learn more about cotton care.